Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism
Category: Abstract Submission
Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism II
287 - Early Versus Late Initiation of Enteral Feeding in Preterm (28-34 weeks GA) Growth Restricted Infants with Absent or Reverse End Diastolic Flow on Umbilical Artery Doppler – A Randomized Control Trial
Friday, April 22, 2022
6:15 PM - 8:45 PM US MT
Poster Number: 287
Publication Number: 287.120
Publication Number: 287.120
Sushma Nangia, Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; Vishnu Mohan M, Lady Hardinge Medical College, New delhi, Delhi, India; Arvind Saili, Lady Hardinge Medical College, New Delhi, Delhi, India; Gunjana Kumar, others, NEW DELHI, India, Delhi, India

Sushma Nangia, MBBS, MD, DM
Neonatologist
Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Early enteral feeding is associated with improved feed tolerance, better postnatal growth, decreased sepsis and early hospital discharge in VLBW infants. However, the incidence of Feed Intolerance (FI), Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) and mortality are reported to be higher in preterm SGA infants, especially with abnormal antenatal Umbilical artery Doppler studies.
Objective: The present study was conducted to examine if early initiation of enteral feeds would result in earlier attainment of full feeds without increase in FI or NEC.
Design/Methods: Preterm SGA infants (28-34 weeks) with absent/reversed end-diastolic flow (AREDF) in antenatal umbilical artery doppler were enrolled in an open labelled RCT and allocated to either Early (at 6 hours of life) Initiation of Enteral Feeding group (EIEF) or Late (at 48 hours of life) Initiation of Enteral Feeding group (LIEF). Measured outcomes were days to reach full feeds (150ml/kg/day) and incidence of FI or NEC. Other outcomes assessed were incidence of sepsis, mortality and duration of hospital stay.
Results: Out of a total of 138 eligible infants who were screened, 87 infants were recruited and randomized to either EIEF or LIEF group (44 vs 43). The median time to achieve full feeds was 2 days earlier in EIEF group when compared to LIEF group (6 days vs. 8 days). The incidence of FI was 20.9% in EIEF group and 25.6% in LIEF group (p = 0.56). Two infants developed NEC stage 3 in the LIEF group whereas no infant developed NEC in EIEF group. Overall incidence of Sepsis was higher in the LIEF group (p=0.02) when compared to EIEF group. Although the incidence of Early onset sepsis was similar but that of Late onset sepsis was significantly higher in the LIEF group (p=0.01). Median (IQR) duration of hospital stay was similar being 23.5 (15.25-29) days in EIEF group as against 23 (17-45) days in LIEF group (p=0.37). Mortality was higher in the LIEF group (17% vs.6.8%) but the difference was not statistically significant.Conclusion(s): Preterm SGA infants with antenatal AREDF can be initiated on enteral feeds as early as 6 hours of life which can be built up quickly with requisite monitoring to reach full feeds by day 6 of life with no increase in FI, NEC, Sepsis or mortality.
Table 1: Primary & Secondary outcomes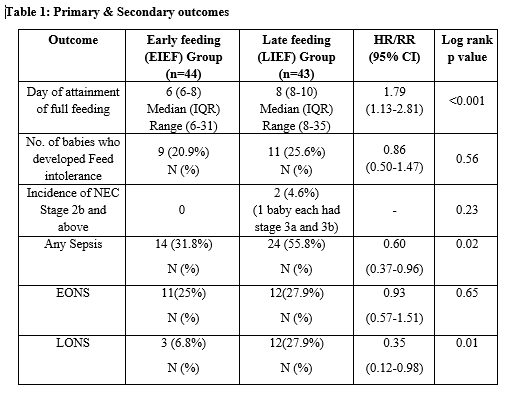
Table 2: Outcome at discharge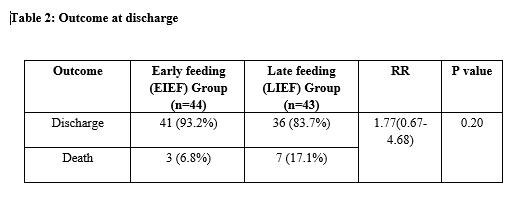
Objective: The present study was conducted to examine if early initiation of enteral feeds would result in earlier attainment of full feeds without increase in FI or NEC.
Design/Methods: Preterm SGA infants (28-34 weeks) with absent/reversed end-diastolic flow (AREDF) in antenatal umbilical artery doppler were enrolled in an open labelled RCT and allocated to either Early (at 6 hours of life) Initiation of Enteral Feeding group (EIEF) or Late (at 48 hours of life) Initiation of Enteral Feeding group (LIEF). Measured outcomes were days to reach full feeds (150ml/kg/day) and incidence of FI or NEC. Other outcomes assessed were incidence of sepsis, mortality and duration of hospital stay.
Results: Out of a total of 138 eligible infants who were screened, 87 infants were recruited and randomized to either EIEF or LIEF group (44 vs 43). The median time to achieve full feeds was 2 days earlier in EIEF group when compared to LIEF group (6 days vs. 8 days). The incidence of FI was 20.9% in EIEF group and 25.6% in LIEF group (p = 0.56). Two infants developed NEC stage 3 in the LIEF group whereas no infant developed NEC in EIEF group. Overall incidence of Sepsis was higher in the LIEF group (p=0.02) when compared to EIEF group. Although the incidence of Early onset sepsis was similar but that of Late onset sepsis was significantly higher in the LIEF group (p=0.01). Median (IQR) duration of hospital stay was similar being 23.5 (15.25-29) days in EIEF group as against 23 (17-45) days in LIEF group (p=0.37). Mortality was higher in the LIEF group (17% vs.6.8%) but the difference was not statistically significant.Conclusion(s): Preterm SGA infants with antenatal AREDF can be initiated on enteral feeds as early as 6 hours of life which can be built up quickly with requisite monitoring to reach full feeds by day 6 of life with no increase in FI, NEC, Sepsis or mortality.
Table 1: Primary & Secondary outcomes

Table 2: Outcome at discharge

