Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology
Category: Abstract Submission
Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology: CMV, HIV, Syphilis, Immunology
317 - Neonatal T cells demonstrate altered mitochondrial respiration following engagement of the T cell receptor
Friday, April 22, 2022
6:15 PM - 8:45 PM US MT
Poster Number: 317
Publication Number: 317.124
Publication Number: 317.124
Jennifer Bermick, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, United States; Matthew Schaller, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL, United States

Jennifer R. Bermick, MD (she/her/hers)
Associate Professor
University of Iowa Health Care
Iowa City, Iowa, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: T cell activation leads to increased mitochondrial respiration, which supports the large increase in gene transcription necessary for a fully functional T cell response. Naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrate altered T cell receptor signaling, including decreased IL-2, IFN-g and CD69 expression compared to adult cells. Because of this, there are currently few vaccines that can be administered in the first two months of life that provide fully functional T cell responses that lead to long-term disease protection. A better understanding of the development and function of naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells and the factors controlling their T cell receptor signaling is needed to optimize neonatal vaccine development and delivery.
Objective: Given the known relationship between T cell activation and mitochondrial respiration, we hypothesized that naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased mitochondrial respiration following engagement of the T cell receptor compared to adult cells.
Design/Methods: Purified naïve CD4+ T cells from human neonates (umbilical cord blood) or healthy adults (peripheral blood) were incubated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads to initiate T cell receptor signaling. T cell responses were measured 24 hours after stimulation using flow cytometry for the cell surface activation marker CD69 and a multiplex protein assay for IL-2, TNF-a and IFN-g expression. Mitochondrial respiration was measured using a Seahorse XF96 Analyzer.
Results: Consistent with previous studies, neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrated decreased IL-2, TNF-a and IFN-g expression and decreased CD69 expression compared to adults (Figure 1). Surprisingly, this decreased neonatal T cell activation was associated with increased baseline mitochondrial respiration and maximal mitochondrial respiration following engagement of the T cell receptor (Figure 2).Conclusion(s): Upon initiation of T cell receptor signaling, naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased markers of activation but increased baseline and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. This suggests that neonatal T cells have the metabolic capacity to activate following engagement of the T cell receptor, and that their lack of activation ability is not due to a failure in mitochondrial respiration. It is possible that the increased mitochondrial respiration seen in the neonatal cells results in enhanced oxidative stress. This oxidative stress could be detrimental to the health of the cells, and could contribute to their decreased ability to activate appropriately, but this needs to be studied further.
Figure 1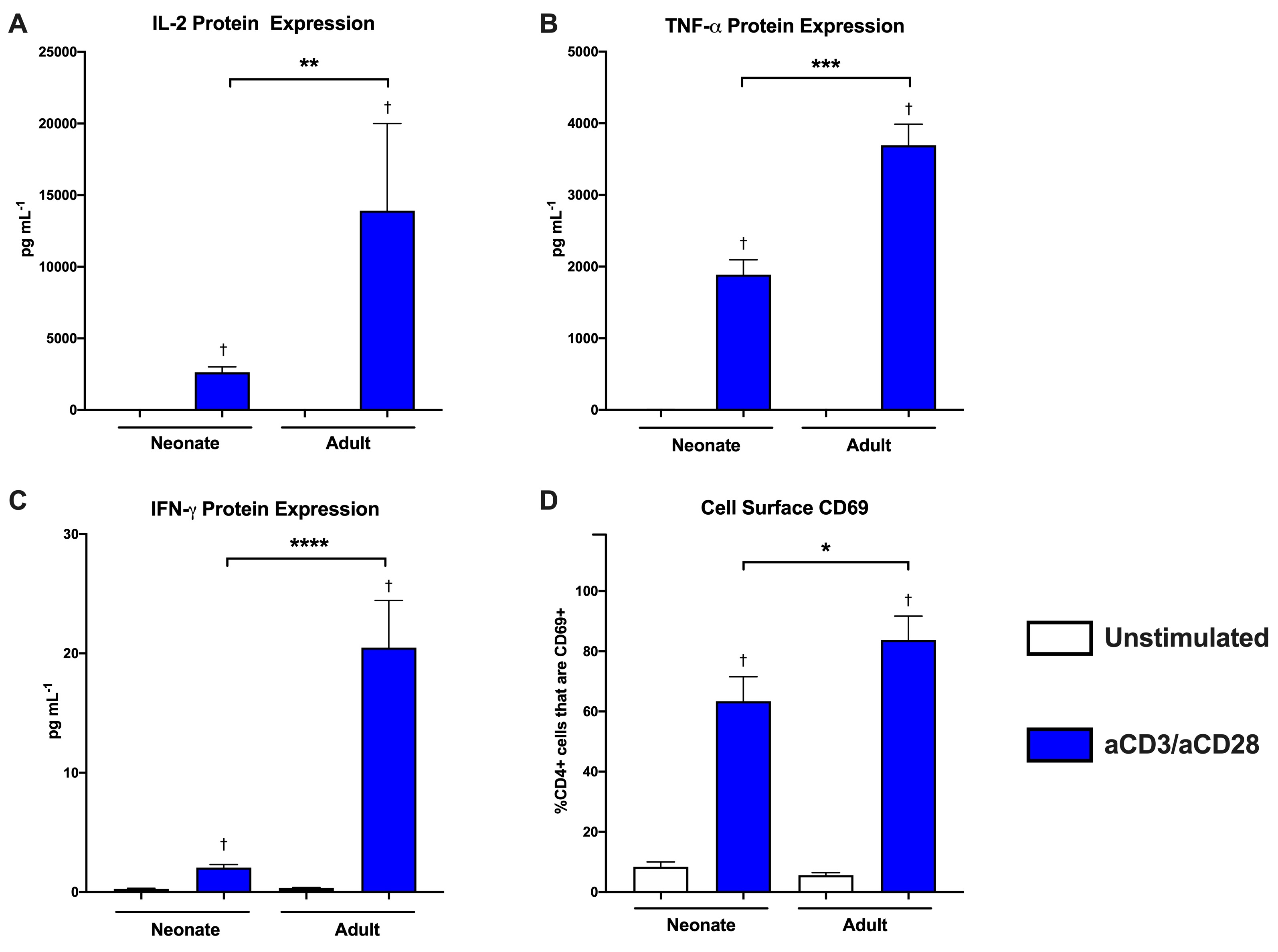 Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased activation following T cell receptor dependent stimulation.
Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased activation following T cell receptor dependent stimulation.
A bead-based multiplex assay was used to measure cytokine protein levels in cell culture supernatants from naïve CD4+ T cells from adults and neonates. Protein expression was measured 24 hours after plating for unstimulated cells and cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. A) IL-2 protein expression, B) TNF-α protein expression and C) IFN-γ protein expression. Neonate (n=5), Adult (n=9). Box represents mean, error bars represent SEM. Differences between groups were measured with the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. †P-value < 0.05 compared to unstimulated control, **P-value < 0.01, ***P-value < 0.001, ****P-value < 0.0001. D) Flow cytometry was used to measure the proportion of naïve CD4+ T cells that were positive for the cell surface marker of activation CD69 in adults and neonates. CD4+CD69+ receptor expression in unstimulated cells or 24 hours after initiation of T cell receptor signaling with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=8), Adult (n=5). Box represents mean, error bars represent SEM. Differences between groups were measured with the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. †P-value < 0.05 compared to unstimulated control, *P-value < 0.05.
Figure 2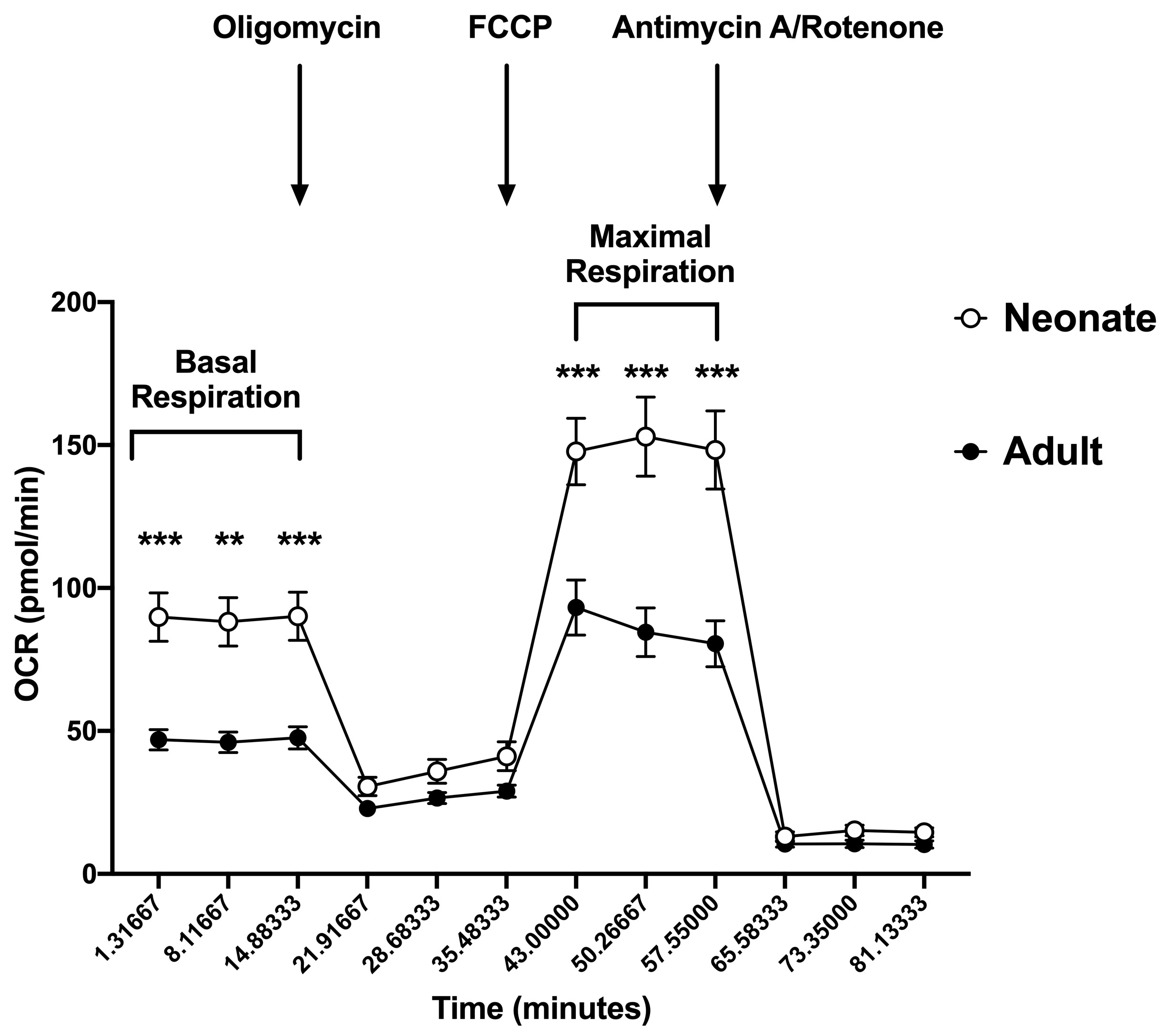 Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrated increased basal and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in adult naïve CD4+ T cells and neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells after sequential injection of oligomycin (3.5 µM), FCCP (2 µM) and antimycin A/rotenone (10 µM) using the Agilent Seahorse XF96 analyzer. T cells were plated at a concentration of 3x105 cells/well and OCR was measured in naïve CD4+ T cells 24 hours after plating in in cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=6), Adult (n=5). Differences between groups were measured using a two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrated increased basal and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in adult naïve CD4+ T cells and neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells after sequential injection of oligomycin (3.5 µM), FCCP (2 µM) and antimycin A/rotenone (10 µM) using the Agilent Seahorse XF96 analyzer. T cells were plated at a concentration of 3x105 cells/well and OCR was measured in naïve CD4+ T cells 24 hours after plating in in cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=6), Adult (n=5). Differences between groups were measured using a two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Objective: Given the known relationship between T cell activation and mitochondrial respiration, we hypothesized that naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased mitochondrial respiration following engagement of the T cell receptor compared to adult cells.
Design/Methods: Purified naïve CD4+ T cells from human neonates (umbilical cord blood) or healthy adults (peripheral blood) were incubated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads to initiate T cell receptor signaling. T cell responses were measured 24 hours after stimulation using flow cytometry for the cell surface activation marker CD69 and a multiplex protein assay for IL-2, TNF-a and IFN-g expression. Mitochondrial respiration was measured using a Seahorse XF96 Analyzer.
Results: Consistent with previous studies, neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrated decreased IL-2, TNF-a and IFN-g expression and decreased CD69 expression compared to adults (Figure 1). Surprisingly, this decreased neonatal T cell activation was associated with increased baseline mitochondrial respiration and maximal mitochondrial respiration following engagement of the T cell receptor (Figure 2).Conclusion(s): Upon initiation of T cell receptor signaling, naïve neonatal CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased markers of activation but increased baseline and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. This suggests that neonatal T cells have the metabolic capacity to activate following engagement of the T cell receptor, and that their lack of activation ability is not due to a failure in mitochondrial respiration. It is possible that the increased mitochondrial respiration seen in the neonatal cells results in enhanced oxidative stress. This oxidative stress could be detrimental to the health of the cells, and could contribute to their decreased ability to activate appropriately, but this needs to be studied further.
Figure 1
 Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased activation following T cell receptor dependent stimulation.
Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrate decreased activation following T cell receptor dependent stimulation. A bead-based multiplex assay was used to measure cytokine protein levels in cell culture supernatants from naïve CD4+ T cells from adults and neonates. Protein expression was measured 24 hours after plating for unstimulated cells and cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. A) IL-2 protein expression, B) TNF-α protein expression and C) IFN-γ protein expression. Neonate (n=5), Adult (n=9). Box represents mean, error bars represent SEM. Differences between groups were measured with the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. †P-value < 0.05 compared to unstimulated control, **P-value < 0.01, ***P-value < 0.001, ****P-value < 0.0001. D) Flow cytometry was used to measure the proportion of naïve CD4+ T cells that were positive for the cell surface marker of activation CD69 in adults and neonates. CD4+CD69+ receptor expression in unstimulated cells or 24 hours after initiation of T cell receptor signaling with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=8), Adult (n=5). Box represents mean, error bars represent SEM. Differences between groups were measured with the Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s multiple comparisons test. †P-value < 0.05 compared to unstimulated control, *P-value < 0.05.
Figure 2
 Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrated increased basal and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in adult naïve CD4+ T cells and neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells after sequential injection of oligomycin (3.5 µM), FCCP (2 µM) and antimycin A/rotenone (10 µM) using the Agilent Seahorse XF96 analyzer. T cells were plated at a concentration of 3x105 cells/well and OCR was measured in naïve CD4+ T cells 24 hours after plating in in cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=6), Adult (n=5). Differences between groups were measured using a two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
Neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells demonstrated increased basal and maximal mitochondrial respiration compared to adult cells. Oxygen consumption rate (OCR) was measured in adult naïve CD4+ T cells and neonatal naïve CD4+ T cells after sequential injection of oligomycin (3.5 µM), FCCP (2 µM) and antimycin A/rotenone (10 µM) using the Agilent Seahorse XF96 analyzer. T cells were plated at a concentration of 3x105 cells/well and OCR was measured in naïve CD4+ T cells 24 hours after plating in in cells stimulated with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads. Neonate (n=6), Adult (n=5). Differences between groups were measured using a two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.