Back
Neonatal Neurology: Translational
Category: Abstract Submission
Neurology 2: Basic-Translational
397 - Dose-response of inter-alpha inhibitor protein treatment after neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury
Saturday, April 23, 2022
3:30 PM – 6:00 PM US MT
Poster Number: 397
Publication Number: 397.236
Publication Number: 397.236
Liam M. Koehn, Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, greensborough, Victoria, Australia; Kevin Nguyen, The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, United States; Xiaodi Chen, The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, United States; Richard Tucker, Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, Providence, RI, United States; Yow-Pin Lim, ProThera Biologics, Inc., Providence, RI, United States; Barbara Stonestreet, Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island, Providence, RI, United States

Liam M. Koehn, PhD
Postdoctoral Fellow
Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island
greensborough, Victoria, Australia
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Hypoxia-ischemia (HI) can damage the neonatal brain, resulting in death or long-term cognitive impairment. Thirty or 60 mg/kg of inter-alpha inhibitor proteins (IAIPs) treatment have been shown to be neuroprotective in neonatal rats exposed to HI. The optimal doses of treatment with IAIPs required to achieve maximal neuroprotection of the brain and improvement in behavioral outcomes has not been determined.
Objective: To compare the efficacy of treatment with 30, 60 or 90 mg/kg IAIPs after exposure to neonatal HI on brain infarct volumes and behavioral performance of righting reflex and small open field tasks. Both male and female cohorts were analyzed to determine whether sex-specific dosing is necessary.
Design/Methods: Postnatal day-7 rats were randomly assigned to 5 groups: sham-placebo (PL), hypoxic/ischemic-PL (HI; right carotid artery ligation, 2 h 8% oxygen), HI-30 mg/kg IAIPs, HI-60 mg/kg IAIPs or HI-90 mg/kg IAIPs (n=10/sex/group). IAIPs or PL were injected IP at zero, 24 and 48 h after HI or sham-normoxia treatment. Righting reflex (24 h after HI, 5 trials) and small open field (72 h after HI, 10 min) were conducted and scored using EthoVision tracking software. Rats were culled at 72 h and brains preserved, sectioned, and stained for cresyl violet. Two observers who were not aware of the assigned study groups measured infarct volume of the hemisphere, cortex and striatum.
Results: HI increased male extension/contraction responses in the small open field tasks and decreased female performance in the righting reflex and small open field exploration tasks (Figure 1). IAIP treatment (30-90 mg/kg) attenuated all behavioral deficits observed, with no notable dose-response. Prominent “responder” and “non-responder” groups were identified for infarct volumes in all treatment groups (Figure 2A) and all brain regions. IAIP attenuation of behavioral deficits correlated with infarct volumes for males (Figure 2B) but not in females.Conclusion(s): Treatment with IAIPs significantly attenuated behavioral deficits in female (righting reflex, small open field exploration) and male (extension/contraction responses) rats after neonatal HI. IAIP attenuation of infarct volume correlates with male preservation of behavior. Further investigation is required to explain female behavioral benefits and “responder” groups in infarct volume measurements. Increasing IAIP dosing from 30 to 90 mg/kg had no notable benefits on behavior or infarct volume after HI.
Liam Koehn (7).pdf
Correlation between male infarct volumes and postural changes after hypoxia ischemia (HI) and inter alpha inhibitor proteins (IAIPs) treatment.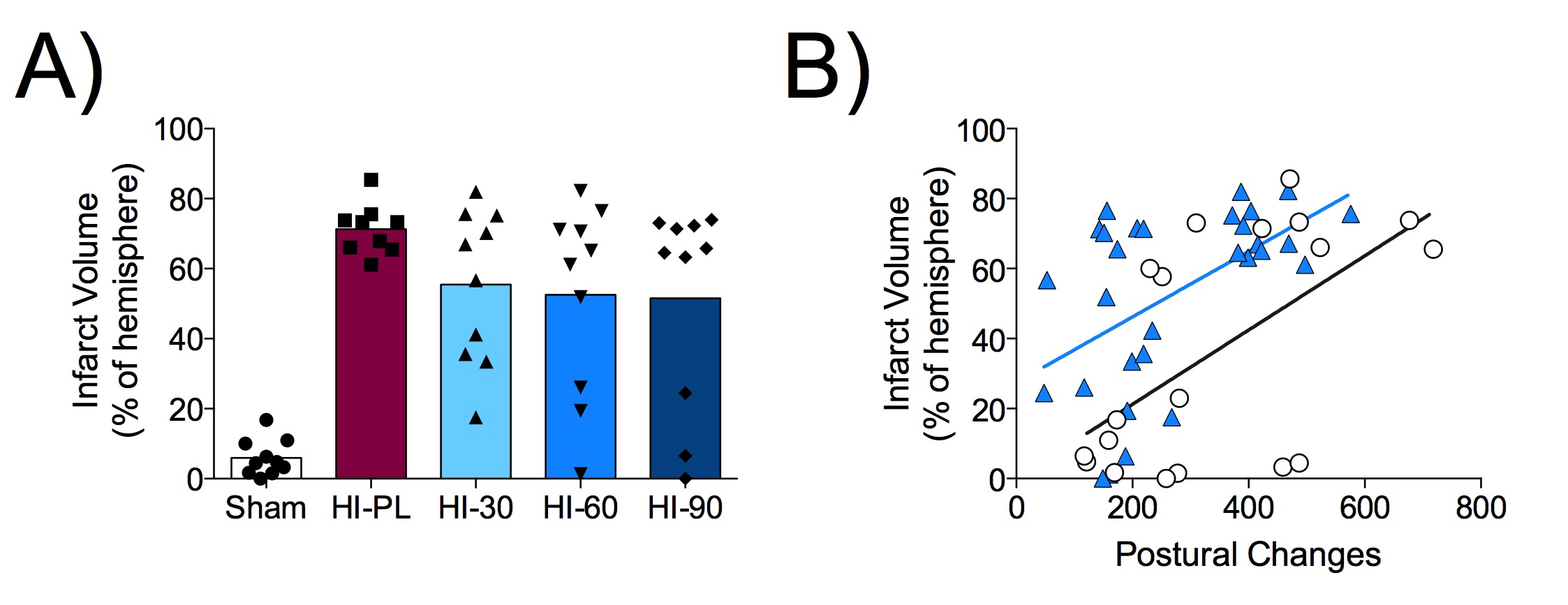 A) Infarct volumes in the right hemisphere of the brain of male neonatal rats after exposure to hypoxia-ischemia (HI), as measured by cresyl violet staining. Results are shown for sham-placebo (PL; sham, open bar), HI-PL (red bar), HI-30 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-30, light blue bar), HI-60 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-60, medium blue bar) and HI-90 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-90, dark blue bar). Statistical analysis was generalized linear models with beta distributions and Tukey-Kramer correction for multiple comparisons. Note “non-responders” (high infarct) and “responders” (low infarct) in IAIP treated groups. B) Correlation of infarct volume measurements with number of elongation or contraction postural changes in open field exploration (10 min). Placebo treated (sham-PL, HI-PL) groups are shown in open circles (black line) and IAIP treated (30, 60 and 90 mg/kg) groups in blue triangles (blue line). Note positive correlation between infarct volume and postural changes for all groups.
A) Infarct volumes in the right hemisphere of the brain of male neonatal rats after exposure to hypoxia-ischemia (HI), as measured by cresyl violet staining. Results are shown for sham-placebo (PL; sham, open bar), HI-PL (red bar), HI-30 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-30, light blue bar), HI-60 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-60, medium blue bar) and HI-90 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-90, dark blue bar). Statistical analysis was generalized linear models with beta distributions and Tukey-Kramer correction for multiple comparisons. Note “non-responders” (high infarct) and “responders” (low infarct) in IAIP treated groups. B) Correlation of infarct volume measurements with number of elongation or contraction postural changes in open field exploration (10 min). Placebo treated (sham-PL, HI-PL) groups are shown in open circles (black line) and IAIP treated (30, 60 and 90 mg/kg) groups in blue triangles (blue line). Note positive correlation between infarct volume and postural changes for all groups.
Objective: To compare the efficacy of treatment with 30, 60 or 90 mg/kg IAIPs after exposure to neonatal HI on brain infarct volumes and behavioral performance of righting reflex and small open field tasks. Both male and female cohorts were analyzed to determine whether sex-specific dosing is necessary.
Design/Methods: Postnatal day-7 rats were randomly assigned to 5 groups: sham-placebo (PL), hypoxic/ischemic-PL (HI; right carotid artery ligation, 2 h 8% oxygen), HI-30 mg/kg IAIPs, HI-60 mg/kg IAIPs or HI-90 mg/kg IAIPs (n=10/sex/group). IAIPs or PL were injected IP at zero, 24 and 48 h after HI or sham-normoxia treatment. Righting reflex (24 h after HI, 5 trials) and small open field (72 h after HI, 10 min) were conducted and scored using EthoVision tracking software. Rats were culled at 72 h and brains preserved, sectioned, and stained for cresyl violet. Two observers who were not aware of the assigned study groups measured infarct volume of the hemisphere, cortex and striatum.
Results: HI increased male extension/contraction responses in the small open field tasks and decreased female performance in the righting reflex and small open field exploration tasks (Figure 1). IAIP treatment (30-90 mg/kg) attenuated all behavioral deficits observed, with no notable dose-response. Prominent “responder” and “non-responder” groups were identified for infarct volumes in all treatment groups (Figure 2A) and all brain regions. IAIP attenuation of behavioral deficits correlated with infarct volumes for males (Figure 2B) but not in females.Conclusion(s): Treatment with IAIPs significantly attenuated behavioral deficits in female (righting reflex, small open field exploration) and male (extension/contraction responses) rats after neonatal HI. IAIP attenuation of infarct volume correlates with male preservation of behavior. Further investigation is required to explain female behavioral benefits and “responder” groups in infarct volume measurements. Increasing IAIP dosing from 30 to 90 mg/kg had no notable benefits on behavior or infarct volume after HI.
Liam Koehn (7).pdf
Correlation between male infarct volumes and postural changes after hypoxia ischemia (HI) and inter alpha inhibitor proteins (IAIPs) treatment.
 A) Infarct volumes in the right hemisphere of the brain of male neonatal rats after exposure to hypoxia-ischemia (HI), as measured by cresyl violet staining. Results are shown for sham-placebo (PL; sham, open bar), HI-PL (red bar), HI-30 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-30, light blue bar), HI-60 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-60, medium blue bar) and HI-90 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-90, dark blue bar). Statistical analysis was generalized linear models with beta distributions and Tukey-Kramer correction for multiple comparisons. Note “non-responders” (high infarct) and “responders” (low infarct) in IAIP treated groups. B) Correlation of infarct volume measurements with number of elongation or contraction postural changes in open field exploration (10 min). Placebo treated (sham-PL, HI-PL) groups are shown in open circles (black line) and IAIP treated (30, 60 and 90 mg/kg) groups in blue triangles (blue line). Note positive correlation between infarct volume and postural changes for all groups.
A) Infarct volumes in the right hemisphere of the brain of male neonatal rats after exposure to hypoxia-ischemia (HI), as measured by cresyl violet staining. Results are shown for sham-placebo (PL; sham, open bar), HI-PL (red bar), HI-30 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-30, light blue bar), HI-60 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-60, medium blue bar) and HI-90 mg/kg IAIP treated (HI-90, dark blue bar). Statistical analysis was generalized linear models with beta distributions and Tukey-Kramer correction for multiple comparisons. Note “non-responders” (high infarct) and “responders” (low infarct) in IAIP treated groups. B) Correlation of infarct volume measurements with number of elongation or contraction postural changes in open field exploration (10 min). Placebo treated (sham-PL, HI-PL) groups are shown in open circles (black line) and IAIP treated (30, 60 and 90 mg/kg) groups in blue triangles (blue line). Note positive correlation between infarct volume and postural changes for all groups.