Back
Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC
Category: Abstract Submission
Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC I
484 - Bovine Lactoferrin preparations and Endotoxin Content: What Is Expected And Safe?
Monday, April 25, 2022
3:30 PM – 6:00 PM US MT
Poster Number: 484
Publication Number: 484.424
Publication Number: 484.424
David A. Kaufman, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, United States; Rachel G. Greenberg, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, NC, United States; David Jensen, Duke University Office of Regulatory Affairs and Quality, Durham, NC, United States

David A. Kaufman, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
University of Virginia School of Medicine
Charlottesville, Virginia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: There is no guidance or recommended testing for endotoxin content in enteral nutrition, supplements or medications. The FDA has given guidance for endotoxin concentration limits for intravenous (IV) dosing of 5 EU/kg/hr (120 EU/kg/day).
Objective: To explore endotoxin content and patient harm, we examined endotoxin content of non-human milk enteral nutrition used in the first weeks in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and bovine lactoferrin (bLF) products. We also examined endotoxin exposure and outcomes in very low birth weight infants.
Design/Methods: Endotoxin content was measured in duplicate using kinetic chromogenic LAL (limulus amebocyte lysate) analysis performed by Charles River Laboratories, Charleston, SC. Dilution in 50% Endotoxin Specific Buffer and 2% saline with heat treatment at 75°C for 10 minutes was performed to eliminate any potential interfering substances.
Results: There is a variation in endotoxin exposure from enteral current formulas used in the NICU between 9 to 334 EU/feed and 75 to 2670 EU/day (based on intake volume of 150 ml/kg/day). In examining one bovine product with an endotoxin content of 10.9 EU/mg produced from whey, the endotoxin exposure was similar to formulas used in preterm infant. There were no cases of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) or adverse effects in 31 patients during lactoferrin administration or hospital mortality.Conclusion(s): Endotoxin can be measured in most enteral nutrition and bovine lactoferrin supplements. Many bLF products have endotoxin content lower than FDA IV limits. Enteral endotoxin daily exposures from bLF do not appear to cause harm.
Table 1.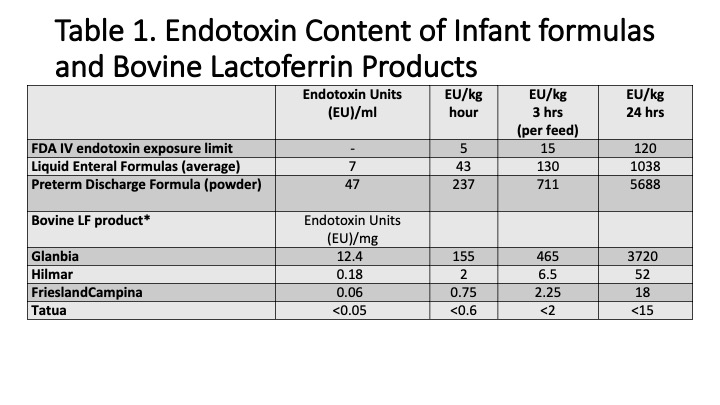
Table 2..jpg)
Objective: To explore endotoxin content and patient harm, we examined endotoxin content of non-human milk enteral nutrition used in the first weeks in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) and bovine lactoferrin (bLF) products. We also examined endotoxin exposure and outcomes in very low birth weight infants.
Design/Methods: Endotoxin content was measured in duplicate using kinetic chromogenic LAL (limulus amebocyte lysate) analysis performed by Charles River Laboratories, Charleston, SC. Dilution in 50% Endotoxin Specific Buffer and 2% saline with heat treatment at 75°C for 10 minutes was performed to eliminate any potential interfering substances.
Results: There is a variation in endotoxin exposure from enteral current formulas used in the NICU between 9 to 334 EU/feed and 75 to 2670 EU/day (based on intake volume of 150 ml/kg/day). In examining one bovine product with an endotoxin content of 10.9 EU/mg produced from whey, the endotoxin exposure was similar to formulas used in preterm infant. There were no cases of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) or adverse effects in 31 patients during lactoferrin administration or hospital mortality.Conclusion(s): Endotoxin can be measured in most enteral nutrition and bovine lactoferrin supplements. Many bLF products have endotoxin content lower than FDA IV limits. Enteral endotoxin daily exposures from bLF do not appear to cause harm.
Table 1.

Table 2.
.jpg)
