Cardiology
Category: Abstract Submission
Cardiology I
169 - Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA) detection in Echocardiograms using Deep Learning
Friday, April 22, 2022
6:15 PM - 8:45 PM US MT
Poster Number: 169
Publication Number: 169.101
Publication Number: 169.101
Howard H. Lei, CHOC Children's Hospital of Orange County, Los Angeles, CA, United States; Amir Ashrafi, CHOC Children's Hospital of Orange County, Newport Coast, CA, United States; Peter D. Chang, University of California, Irvine, School of Medicine, Irvine, CA, United States; Anthony Chang, CHOC, Orange, CA, United States; Wyman W. Lai, University of California, Irvine, School of Medicine, Orange, CA, United States

Howard H. Lei, Ph.D.
Senior Data Scientist
CHOC Children's Hospital of Orange County
Los Angeles, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a common form of congenital heart disease, especially in preterm infants. A PDA can be associated with prolonged ventilator dependence and increased risk of severe lung disease, necrotizing enterocolitis, impaired renal function, intraventricular hemorrhage, and death. The problem of managing neonates with a PDA is difficult, and the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to aid in PDA detection can assist in its management.
Objective: As a first step to developing an AI-based approach towards improving the management of PDA patients, we developed a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for detecting the presence of PDAs in echocardiogram scans of preterm infants. The CNN is used given its proven effectiveness for image-based object detection and classification. Furthermore, we aimed to develop an approach that is suitable for eventual clinical deployment within an edge-based framework.
Design/Methods: A clinical database was searched for echocardiograms performed in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) at the Children’s Hospital of Orange County (CHOC) from 2017-21. A total of 461 de-identified echocardiogram video clips across 300 patients from CHOC were analyzed. For our CNN-based approach to be deployable within an edge-based framework, we used the light-weight MobileNet-V2 CNN architecture for training, validation, and testing. Of the 461 echocardiogram video clips, 316 were used for training, 74 for validation, and 72 for testing. 272 of the 461 video clips contained an identifiable PDA and 190 were considered normal. Video frames were extracted from each video clip and processed by the CNN. The CNN first provided 2-class (Normal vs PDA) classification scores for each video frame. These scores are then aggregated to provide an overall Normal vs PDA label for each video clip.
Results: Our MobileNet-V2 CNN algorithm achieved notable results for identifying the presence of a PDA, with 0.88 Area Under Curve (AUC), 0.84 Positive Predictive Value (PPV), 0.80 Negative Predictive Value (NPV), 0.76 Sensitivity, and 0.87 Specificity on the test data. A statistical t-test using the CNN-generated scores on the test data showed that the distribution of scores from the two classes are significantly different with p< < 0.05.Conclusion(s): This work demonstrated that the diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in neonatal echocardiograms using AI-based algorithms is feasible. Future work involves expanding the dataset, and fine-tuning our algorithms to improve classification accuracy and to detect additional artifacts in echocardiogram scans.
Sample echocardiogram video frames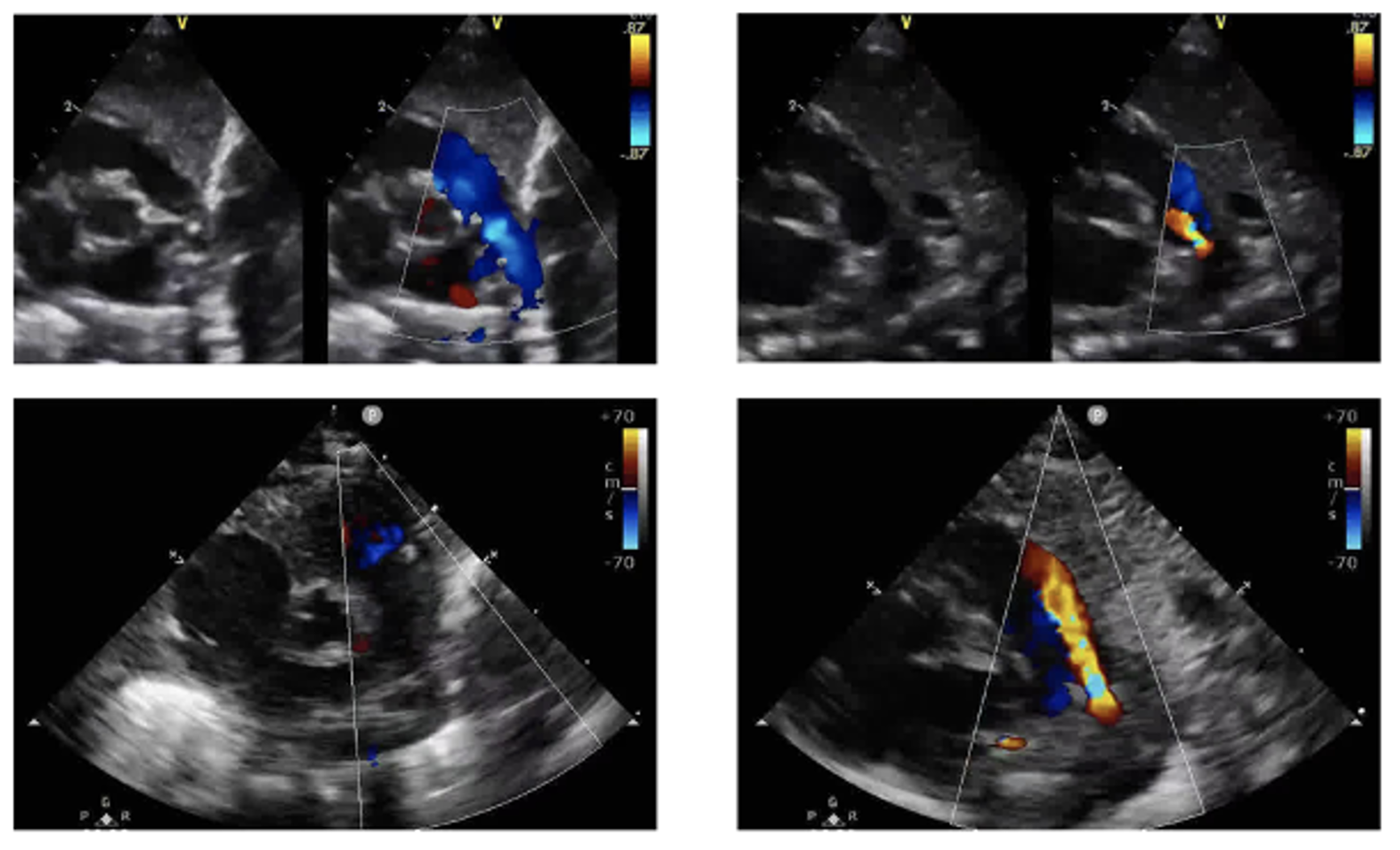 This figure shows four sample echocardiogram video frames. The two images on the right of Figure 3 show examples of a PDA, while the images on the left do not contain a PDA. The PDA is indicated by the red-colored flow pattern during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The two images in the top row of Figure 3 are color-compare scans. They contain two scans side-by-side, one with color Doppler flow mapping and one without color Doppler. The two scans in the bottom row contain non-color compare scans, with just a single scan showing colored Doppler flow mapping. The goal of this work is to indiscriminately handle the color-compare and non-color compare scans, as both are encountered in real-world scenarios.
This figure shows four sample echocardiogram video frames. The two images on the right of Figure 3 show examples of a PDA, while the images on the left do not contain a PDA. The PDA is indicated by the red-colored flow pattern during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The two images in the top row of Figure 3 are color-compare scans. They contain two scans side-by-side, one with color Doppler flow mapping and one without color Doppler. The two scans in the bottom row contain non-color compare scans, with just a single scan showing colored Doppler flow mapping. The goal of this work is to indiscriminately handle the color-compare and non-color compare scans, as both are encountered in real-world scenarios.
CNN-based classification of echocardiogram video frames as independent images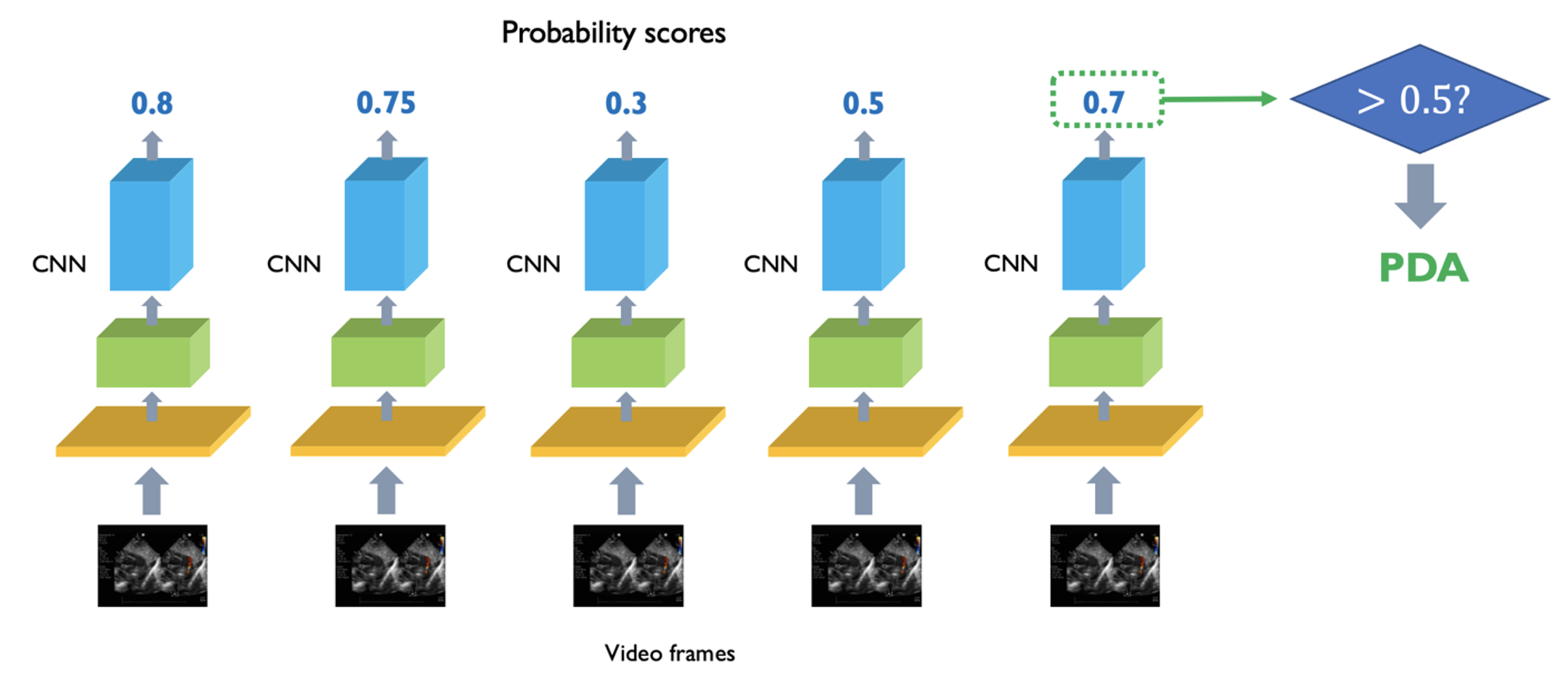 Processing of video clip frames as independent images using the MobileNet-V2 CNN. The CNN generates a probably score for each video frame, indicating the probability of whether the video frame contains a PDA. If the probability exceeds 50%, the video frame is classified as containing a PDA.
Processing of video clip frames as independent images using the MobileNet-V2 CNN. The CNN generates a probably score for each video frame, indicating the probability of whether the video frame contains a PDA. If the probability exceeds 50%, the video frame is classified as containing a PDA.
Objective: As a first step to developing an AI-based approach towards improving the management of PDA patients, we developed a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for detecting the presence of PDAs in echocardiogram scans of preterm infants. The CNN is used given its proven effectiveness for image-based object detection and classification. Furthermore, we aimed to develop an approach that is suitable for eventual clinical deployment within an edge-based framework.
Design/Methods: A clinical database was searched for echocardiograms performed in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) at the Children’s Hospital of Orange County (CHOC) from 2017-21. A total of 461 de-identified echocardiogram video clips across 300 patients from CHOC were analyzed. For our CNN-based approach to be deployable within an edge-based framework, we used the light-weight MobileNet-V2 CNN architecture for training, validation, and testing. Of the 461 echocardiogram video clips, 316 were used for training, 74 for validation, and 72 for testing. 272 of the 461 video clips contained an identifiable PDA and 190 were considered normal. Video frames were extracted from each video clip and processed by the CNN. The CNN first provided 2-class (Normal vs PDA) classification scores for each video frame. These scores are then aggregated to provide an overall Normal vs PDA label for each video clip.
Results: Our MobileNet-V2 CNN algorithm achieved notable results for identifying the presence of a PDA, with 0.88 Area Under Curve (AUC), 0.84 Positive Predictive Value (PPV), 0.80 Negative Predictive Value (NPV), 0.76 Sensitivity, and 0.87 Specificity on the test data. A statistical t-test using the CNN-generated scores on the test data showed that the distribution of scores from the two classes are significantly different with p< < 0.05.Conclusion(s): This work demonstrated that the diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in neonatal echocardiograms using AI-based algorithms is feasible. Future work involves expanding the dataset, and fine-tuning our algorithms to improve classification accuracy and to detect additional artifacts in echocardiogram scans.
Sample echocardiogram video frames
 This figure shows four sample echocardiogram video frames. The two images on the right of Figure 3 show examples of a PDA, while the images on the left do not contain a PDA. The PDA is indicated by the red-colored flow pattern during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The two images in the top row of Figure 3 are color-compare scans. They contain two scans side-by-side, one with color Doppler flow mapping and one without color Doppler. The two scans in the bottom row contain non-color compare scans, with just a single scan showing colored Doppler flow mapping. The goal of this work is to indiscriminately handle the color-compare and non-color compare scans, as both are encountered in real-world scenarios.
This figure shows four sample echocardiogram video frames. The two images on the right of Figure 3 show examples of a PDA, while the images on the left do not contain a PDA. The PDA is indicated by the red-colored flow pattern during the diastolic phase of the cardiac cycle. The two images in the top row of Figure 3 are color-compare scans. They contain two scans side-by-side, one with color Doppler flow mapping and one without color Doppler. The two scans in the bottom row contain non-color compare scans, with just a single scan showing colored Doppler flow mapping. The goal of this work is to indiscriminately handle the color-compare and non-color compare scans, as both are encountered in real-world scenarios.CNN-based classification of echocardiogram video frames as independent images
 Processing of video clip frames as independent images using the MobileNet-V2 CNN. The CNN generates a probably score for each video frame, indicating the probability of whether the video frame contains a PDA. If the probability exceeds 50%, the video frame is classified as containing a PDA.
Processing of video clip frames as independent images using the MobileNet-V2 CNN. The CNN generates a probably score for each video frame, indicating the probability of whether the video frame contains a PDA. If the probability exceeds 50%, the video frame is classified as containing a PDA.