Child Abuse & Neglect
Category: Abstract Submission
Child Abuse & Neglect I
218 - Comparison of Risk for Child Sex Trafficking Among Adolescents from Different Metropolitan Settings and Chief Complaints
Monday, April 25, 2022
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM US MT
Poster Number: 218
Publication Number: 218.401
Publication Number: 218.401
Paul McPherson, Akron Children's Hospital, Akron, OH, United States; Serena DiMattia, Akron Children's Hospital, Wadsworth, OH, United States

Serena Wagoner, DO
PGY-2
Akron Children's Hospital
Wadsworth, Ohio, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Child sex trafficking (CST) is a recognized societal problem. Up to 88% of CST victims report seeking medical care while being trafficked. CST screening studies focus on large urban emergency departments. Few studies have examined patients from smaller populations and different clinical settings. Studies screening for CST in foster care populations are lacking.
Objective: Identify rate for risk of CST for patients from 3 different child abuse clinics (CAC), representing two different metropolitan settings (2 from medium regions and 1 from micro-medium region) that present for evaluation.
Design/Methods: A validated 6 question CST screening tool was administered to patients 12 to 18 years old presenting to one of three hospital CACs from Aug 2020 – Oct 2021. Chief complaints included child sexual abuse, physical abuse, or foster care placement exams. A positive screen was defined as three affirmative responses. Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test were utilized for categorical data analysis, Student’s t-test for continuous data analysis. Binary logistic regression was used to assess factors associated with positive screening.
Results: Total of 495 patients were screened. 15.4% screened positive. Positive screens were associated with age, health insurance and metropolitan size. Age and Medicaid users remained significant with regression analysis. Other variables were investigated (race, ethnicity, gender, chief complaint), but were not significant predictors of positive screening. Significant CST risk differentials between one of the medium vs. micro-medium metro regions dropped in regression analysis. Positive risk for CST screens for sexual abuse vs foster care were 18.3% and 18.8% respectively.Conclusion(s): There is no significant risk differential for CST among patients evaluated for foster care placement compared to suspected abuse victims. Adolescents from micro-medium metropolitan settings have similar risk to one of the larger metropolitan regions. Adoption of CST screening procedures beyond the ED setting and larger metropolitan regions will identify at risk youth.
Demographics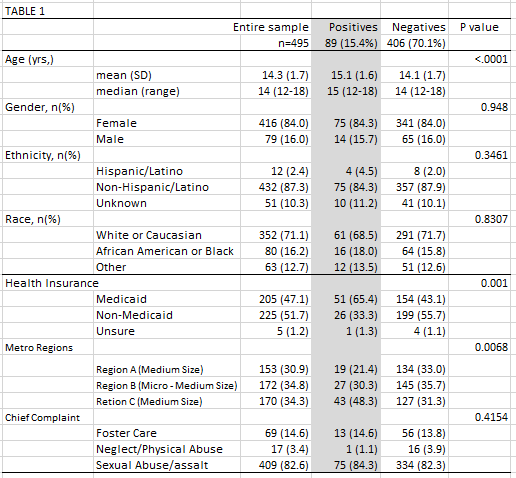
Regression Analysis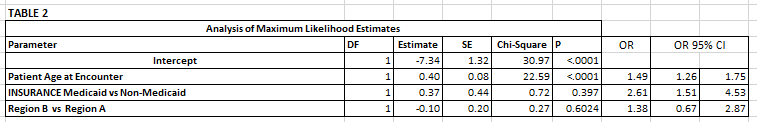
Objective: Identify rate for risk of CST for patients from 3 different child abuse clinics (CAC), representing two different metropolitan settings (2 from medium regions and 1 from micro-medium region) that present for evaluation.
Design/Methods: A validated 6 question CST screening tool was administered to patients 12 to 18 years old presenting to one of three hospital CACs from Aug 2020 – Oct 2021. Chief complaints included child sexual abuse, physical abuse, or foster care placement exams. A positive screen was defined as three affirmative responses. Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test were utilized for categorical data analysis, Student’s t-test for continuous data analysis. Binary logistic regression was used to assess factors associated with positive screening.
Results: Total of 495 patients were screened. 15.4% screened positive. Positive screens were associated with age, health insurance and metropolitan size. Age and Medicaid users remained significant with regression analysis. Other variables were investigated (race, ethnicity, gender, chief complaint), but were not significant predictors of positive screening. Significant CST risk differentials between one of the medium vs. micro-medium metro regions dropped in regression analysis. Positive risk for CST screens for sexual abuse vs foster care were 18.3% and 18.8% respectively.Conclusion(s): There is no significant risk differential for CST among patients evaluated for foster care placement compared to suspected abuse victims. Adolescents from micro-medium metropolitan settings have similar risk to one of the larger metropolitan regions. Adoption of CST screening procedures beyond the ED setting and larger metropolitan regions will identify at risk youth.
Demographics

Regression Analysis

