Emergency Medicine: All Areas
Category: Abstract Submission
Emergency Medicine VII
366 - Appropriateness of Use of Streptococcal Pharyngitis Testing and Associated Antibiotic Prescribing in the Urgent Care (UC) Setting
Saturday, April 23, 2022
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM US MT
Poster Number: 366
Publication Number: 366.206
Publication Number: 366.206
Michael A. Haynes, Phoenix Children's Hospital, SCOTTSDALE, AZ, United States; Igor Kushner, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Hamy Temkit, Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, United States; Diane E. Hindman, Phoenix Children's Hospital, Mesa, AZ, United States
- MH
Michael A. Haynes, DO MHM (he/him/his)
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Fellow
Phoenix Children's Hospital
SCOTTSDALE, Arizona, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Pharyngitis due to Group A Beta-hemolytic Streptococcus (GAS) is a common diagnosis in the pediatric population. Scoring systems and guidelines were implemented for guidance of appropriate administration of Streptococcal Rapid Antigen Detection Tests (RADTs). Patients often receive inappropriate testing as guidelines are not followed. This presents an unnecessary monetary burden on the patient and healthcare system. Indiscriminate testing also puts patients at risk for unwarranted antibiotic use.
Objective: The primary objective was to evaluate the proportion and circumstances of inappropriate RADTs performed based on Modified Centor Criteria and Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines at Phoenix Children’s Hospital (PCH) Urgent Care clinics. A secondary objective was determining the rate of inappropriate use of antibiotics based on RADTs results.
Design/Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted from July 1, 2018 to June 30, 2019 of RADTs performed on patients under 19 years old at the PCH Urgent Care clinics. Data was collected using a REDCap database. Proportions of variables of interest are provided with 95% confidence intervals and a statistical significance level of 0.05. Analysis was conducted with Chi-squared and McNemar’s test.
Results: A total of 1500 patients were reviewed, and 1380 RADTs performed with a positivity rate of 43.8%. Fifty-nine percent of RADTs were performed on patients with a Modified Centor Score < 3 (p < 0.0001). For a Modified Centor Score >=3, 52.1% were positive for necessary tests with a negativity rate of 32% (p < 0.0001). Roughly 3% of negative RADTs had a positive confirmatory culture. Of the total 1500 patients, 108 patients were under the age of 3 years and 82 of these patients had a RADT for pharyngitis. Roughly 46% of patients under 3 tested were positive for GAS. Only 15 patients under the age of 3 tested had an exposure to GAS. A total of 691 antibiotic prescriptions were given for GAS pharyngitis treatment. Of these, 28 prescriptions were given to patients with symptoms or exposure without a RADT or culture. Another 44 prescriptions were given to patients with a negative RADT and culture.Conclusion(s): Over 50% of RADTs performed at PCH Urgent Care clinics were inappropriate per clinical guidelines. Due to these inappropriate rapid tests, $1500 was spent unnecessarily on confirmatory cultures. PCH plans to do a quality initiative to correct this issue.
Michael Haynes CVMichael Haynes CV 2021 copy.pdf
Sensitivity and Specificity of the Centor Score < 3 vs ≥3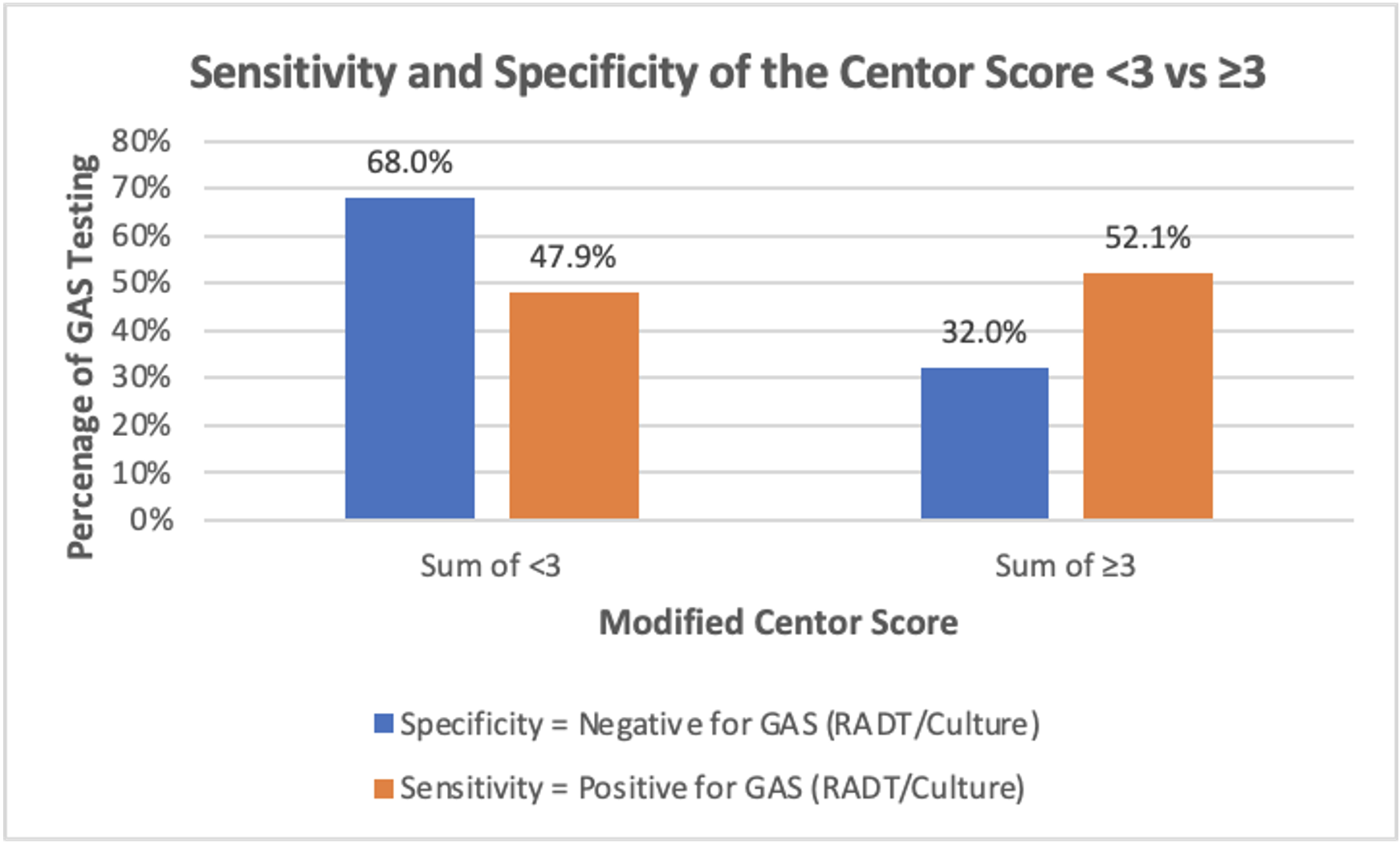 Association between a Modified Centor Score < 3 and ≥3 with sensitivity and specificity (p-value < 0.0001)
Association between a Modified Centor Score < 3 and ≥3 with sensitivity and specificity (p-value < 0.0001)
Objective: The primary objective was to evaluate the proportion and circumstances of inappropriate RADTs performed based on Modified Centor Criteria and Infectious Diseases Society of America clinical practice guidelines at Phoenix Children’s Hospital (PCH) Urgent Care clinics. A secondary objective was determining the rate of inappropriate use of antibiotics based on RADTs results.
Design/Methods: A retrospective chart review was conducted from July 1, 2018 to June 30, 2019 of RADTs performed on patients under 19 years old at the PCH Urgent Care clinics. Data was collected using a REDCap database. Proportions of variables of interest are provided with 95% confidence intervals and a statistical significance level of 0.05. Analysis was conducted with Chi-squared and McNemar’s test.
Results: A total of 1500 patients were reviewed, and 1380 RADTs performed with a positivity rate of 43.8%. Fifty-nine percent of RADTs were performed on patients with a Modified Centor Score < 3 (p < 0.0001). For a Modified Centor Score >=3, 52.1% were positive for necessary tests with a negativity rate of 32% (p < 0.0001). Roughly 3% of negative RADTs had a positive confirmatory culture. Of the total 1500 patients, 108 patients were under the age of 3 years and 82 of these patients had a RADT for pharyngitis. Roughly 46% of patients under 3 tested were positive for GAS. Only 15 patients under the age of 3 tested had an exposure to GAS. A total of 691 antibiotic prescriptions were given for GAS pharyngitis treatment. Of these, 28 prescriptions were given to patients with symptoms or exposure without a RADT or culture. Another 44 prescriptions were given to patients with a negative RADT and culture.Conclusion(s): Over 50% of RADTs performed at PCH Urgent Care clinics were inappropriate per clinical guidelines. Due to these inappropriate rapid tests, $1500 was spent unnecessarily on confirmatory cultures. PCH plans to do a quality initiative to correct this issue.
Michael Haynes CVMichael Haynes CV 2021 copy.pdf
Sensitivity and Specificity of the Centor Score < 3 vs ≥3
 Association between a Modified Centor Score < 3 and ≥3 with sensitivity and specificity (p-value < 0.0001)
Association between a Modified Centor Score < 3 and ≥3 with sensitivity and specificity (p-value < 0.0001)