General Pediatrics: All Areas
Category: Abstract Submission
General Pediatrics IV
187 - The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Acute Appendicitis Presentation in Two Urban Multiethnic Community Hospitals
Sunday, April 24, 2022
3:30 PM - 6:00 PM US MT
Poster Number: 187
Publication Number: 187.317
Publication Number: 187.317
Priya Mallikarjuna, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States; Saikat Goswami, flushing hospital medical center, Flushing, NY, United States; Radhika Maddali, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States; Sandy Ma, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States; Won H. Baik-Han, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States; Kelly L. Cervellione, MediSys Management, Jamaica, NY, United States; Lily Q. Lew, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States; Gagan Gulati, Flushing Hospital Medical Center, Flushing, NY, United States

Priya Mallikarjuna, MD, MA (she/her/hers)
Resident
Flushing Hospital Medical Center
New York, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Acute appendicitis (AA) is the most common abdominal surgical emergency in pediatrics. There was a precipitous drop in pediatric visits to hospitals, including the emergency department, since the US declared COVID-19 a national emergency. Managing AA during the pandemic remains a challenge as fear of COVID exposure can lead to delays in presentation and surgery, as well as a shift to conservative management. Alvarado score (AS) is a ten-point clinical scoring system to identify AA and the American Association for the Surgery of Trauma (AAST) grading system (I-V) are validated tools for AA diagnosis and severity. There are no studies on prevalence and severity of AA during the COVID-19 pandemic in an urban multiethnic community.
Objective: To compare prevalence and severity of AA before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Design/Methods: This was a retrospective chart review of patients admitted to Flushing Hospital Medical Center and Jamaica Hospital Medical Center with the diagnosis of AA from March 2018 to March 2021. Charts were reviewed for demographics, clinical, imaging and surgical data to determine AS and AAST. AS grouped from 1-6 (less likely to require surgery) and 7-10 (more likely to require surgery). AAST scoring was based on most severe criteria if grading discrepancies were found between pathology, surgical and computed tomography findings. Leukocytosis was defined as white blood cell count >10. G1 identified AA cases March 2018 - February 2020 and G2 March 2020 – March 2021. Data was analyzed using SPSS software, p< 0.05 considered significant.
Results: Of 239 patients with AA over 3 years, G1 totaled 184 (77%) in 2 years pre-pandemic and G2 had 55 (23%) during first year pandemic. Mean age, gender and ethnicity were similar for G1 and G2. AS and AAST were compared for G1 and G2, Table 1. G2 had significantly greater overall AS of >7 (p=0.038) and higher AAST (p=0.016). Only three patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and 9 (16%) of G2 were transferred to a tertiary care center. Conclusion(s): Although there was a decline in number of AA evaluated in our emergency department, the severity of AA was heightened during the pandemic. Healthcare providers need to have a high index of suspicion of increased severity with complications of AA.
Alvarado and AAST Scoring In G1 and G2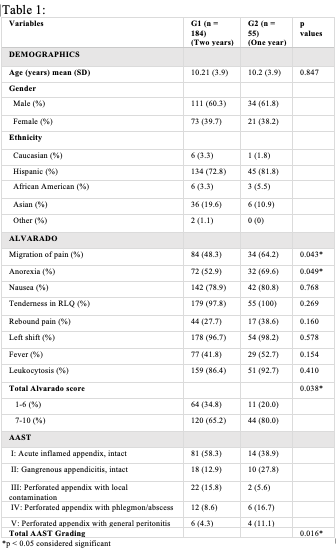
Objective: To compare prevalence and severity of AA before and during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Design/Methods: This was a retrospective chart review of patients admitted to Flushing Hospital Medical Center and Jamaica Hospital Medical Center with the diagnosis of AA from March 2018 to March 2021. Charts were reviewed for demographics, clinical, imaging and surgical data to determine AS and AAST. AS grouped from 1-6 (less likely to require surgery) and 7-10 (more likely to require surgery). AAST scoring was based on most severe criteria if grading discrepancies were found between pathology, surgical and computed tomography findings. Leukocytosis was defined as white blood cell count >10. G1 identified AA cases March 2018 - February 2020 and G2 March 2020 – March 2021. Data was analyzed using SPSS software, p< 0.05 considered significant.
Results: Of 239 patients with AA over 3 years, G1 totaled 184 (77%) in 2 years pre-pandemic and G2 had 55 (23%) during first year pandemic. Mean age, gender and ethnicity were similar for G1 and G2. AS and AAST were compared for G1 and G2, Table 1. G2 had significantly greater overall AS of >7 (p=0.038) and higher AAST (p=0.016). Only three patients tested positive for SARS-CoV-2 and 9 (16%) of G2 were transferred to a tertiary care center. Conclusion(s): Although there was a decline in number of AA evaluated in our emergency department, the severity of AA was heightened during the pandemic. Healthcare providers need to have a high index of suspicion of increased severity with complications of AA.
Alvarado and AAST Scoring In G1 and G2

